Acute Dental Concerns
Toothache
Clean area gently; rinsing with warm water may help to dislodge any impacted food. It is best for your child to eat on the other side of their mouth until you can see your family dentist. Your usual sugar-free pain relief may also help (e.g. Calpol, Nurofen).
If your child’s face is swollen contact your family dentist.
Chipped, Broken or Bumped Tooth
It is best to contact a dentist for advice in these cases. In some instances the dentist will recommend your child is seen immediately, in other cases it won’t be as urgent. However, it is best to get the dentist to check any traumatic injury to the teeth as soon as possible.
We would strongly advise that parents avail of 24 hour school insurance for their children. The fee is very reasonable and provides good cover for dental injuries.
Child’s Baby Tooth Knocked Out
If a baby tooth is knocked out do not try and put it back. If you do try and put it back you may accidentally damage the adult tooth that is developing in the gum. It is always a good idea to contact your family dentist.
Child’s Adult Tooth is Knocked Out
Unlike baby teeth, if a permanent tooth is knocked out it should be replaced in the socket immediately. Once replaced correctly, have the child hold the tooth in place by biting on gauze / soft cloth. The longer the tooth is out of the mouth, the lower the chance of long-term survival. If you are unable to put the tooth back, place it into milk and see the dentist as soon as possible.
Note: Do not clean the tooth with soap or handle the root unnecessarily.
Cut or Bitten Tongue, Lip or Cheek
Apply ice to injured areas to help control swelling. If there is bleeding, apply firm but gentle pressure with a gauze or cloth. If bleeding cannot be controlled by simple pressure – call a doctor or visit the hospital emergency room.

Severe Blow to the Head
Take your child to the nearest hospital emergency room immediately.
Possible Broken or Fractured Jaw
Keep the jaw from moving and take your child to the nearest hospital emergency room.
Dental trauma is common in children.
It is important that oral / dental injuries are checked by the Dentist as soon as possible.
Trauma to Primary (Baby) Teeth
Before
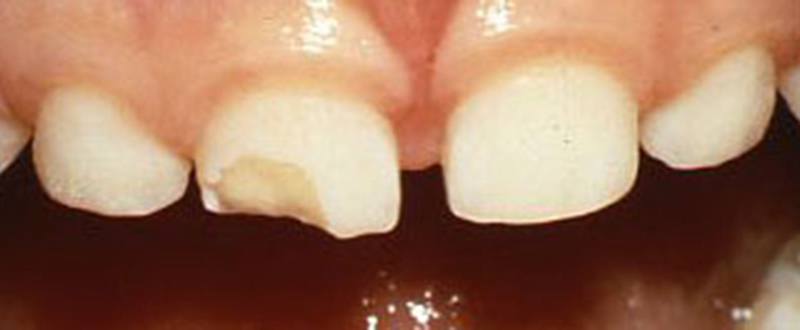 3 year old girl who fell and broke her upper primary (baby) tooth.
3 year old girl who fell and broke her upper primary (baby) tooth.
After
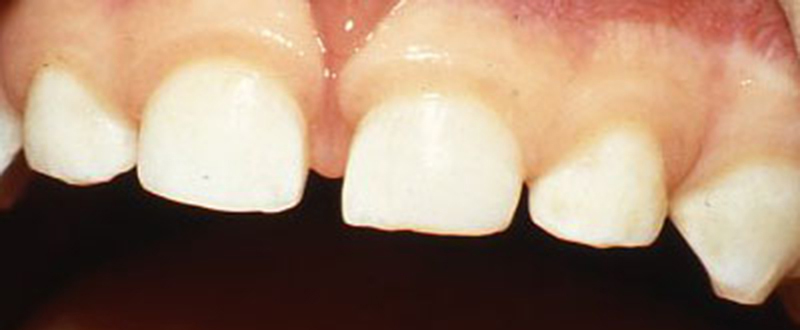 Repaired with composite (white) filling material.
Repaired with composite (white) filling material.
Trauma To Baby Teeth
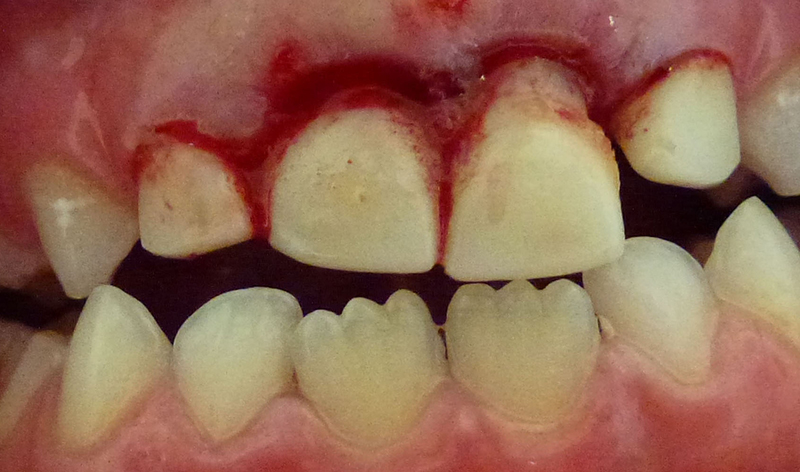 6 year old boy who fell off his bike and bumped his two front primary (baby) teeth.
6 year old boy who fell off his bike and bumped his two front primary (baby) teeth.
Permanent Teeth Erupting
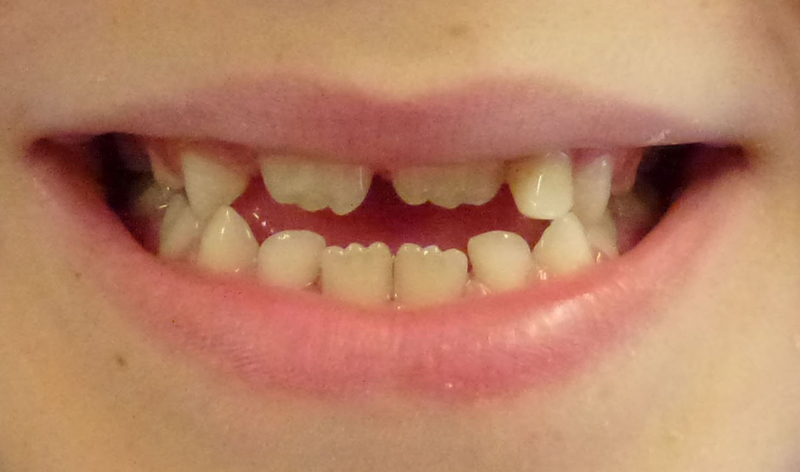 3 months later, all recovered and permanent (adult) teeth have erupted into correct position.
3 months later, all recovered and permanent (adult) teeth have erupted into correct position.
Defects on Permanent (Adult) Teeth
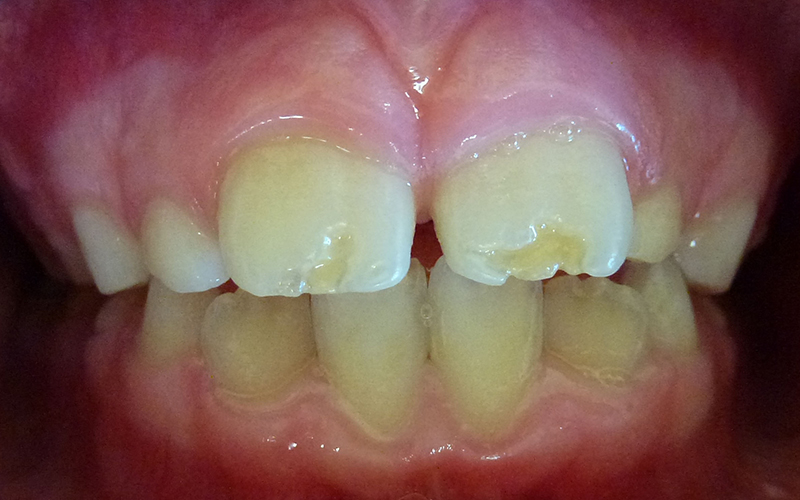 The original trauma to his primary (baby) teeth had damaged his permanent (adult) front teeth.
The original trauma to his primary (baby) teeth had damaged his permanent (adult) front teeth.
Repaired Defects
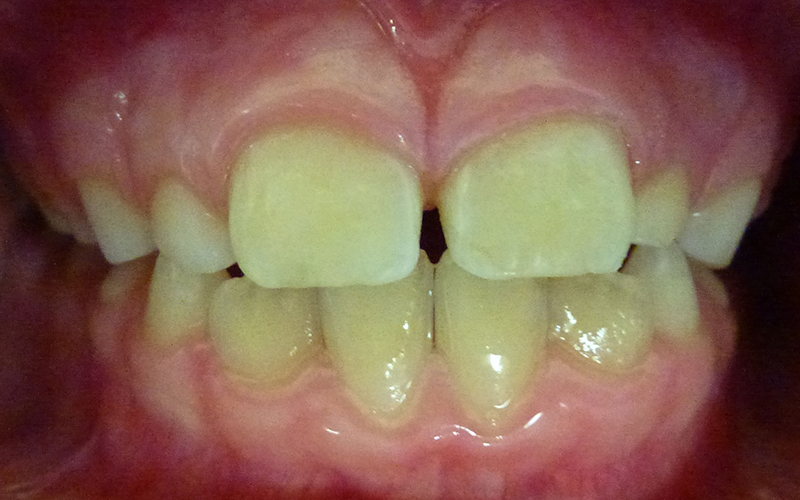 This was easily repaired with composite (white) filling material.
This was easily repaired with composite (white) filling material.
Damage to the edges of permanent (adult) front teeth in a young child, caused by injury to their primary (baby) teeth at a very young age (approx. 1-2 years). It is important that a Dentist checks your child if they injure their teeth / mouth.
Trauma to Permanent Teeth
Before
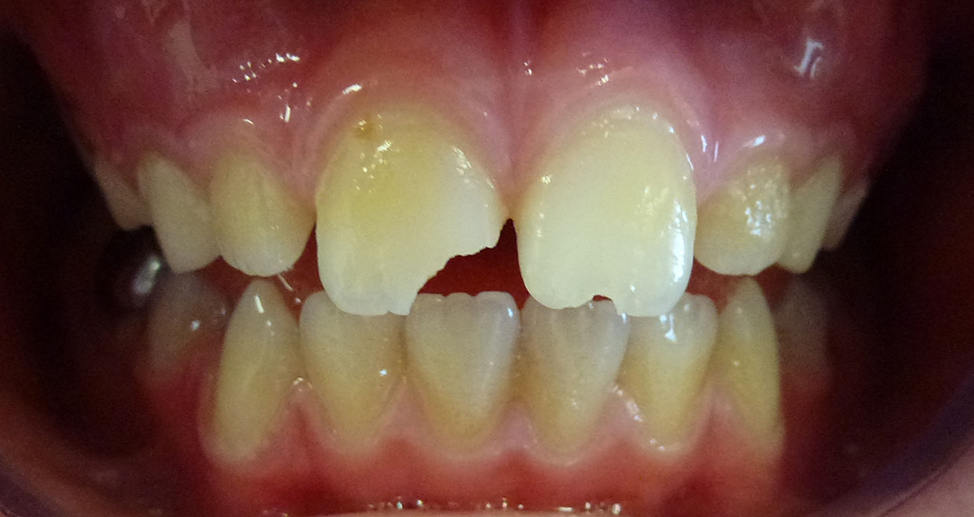 8 year old girl, who fell playing on concrete, fractured 2 upper permanent (adult) teeth, one tooth fractured more extensively than the other.
8 year old girl, who fell playing on concrete, fractured 2 upper permanent (adult) teeth, one tooth fractured more extensively than the other.
After
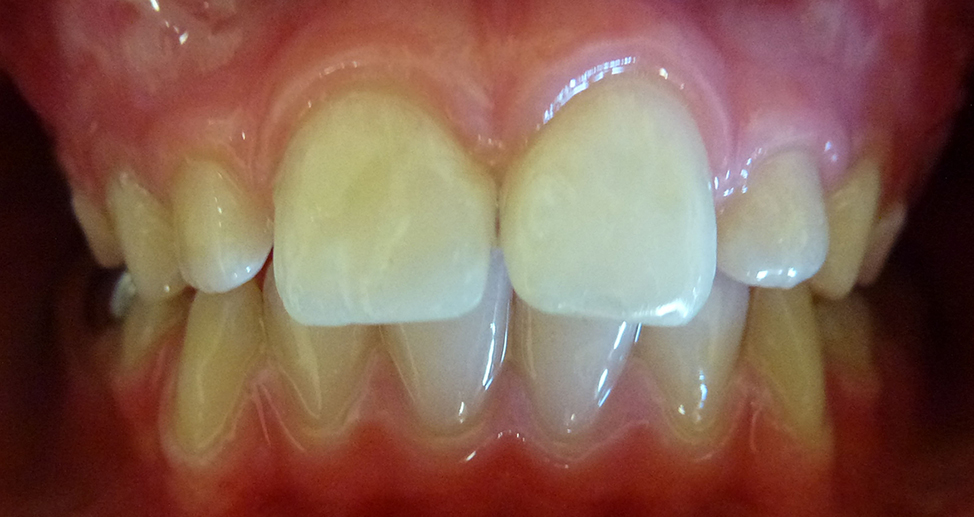 Both teeth repaired using composite (white) filling material.
Both teeth repaired using composite (white) filling material.
Before
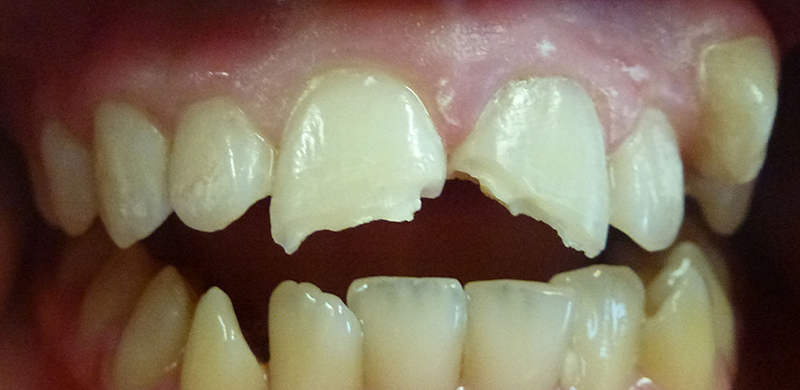 13 year old boy who fell playing sport, broke 2 upper permanent (adult) teeth.
13 year old boy who fell playing sport, broke 2 upper permanent (adult) teeth.
After
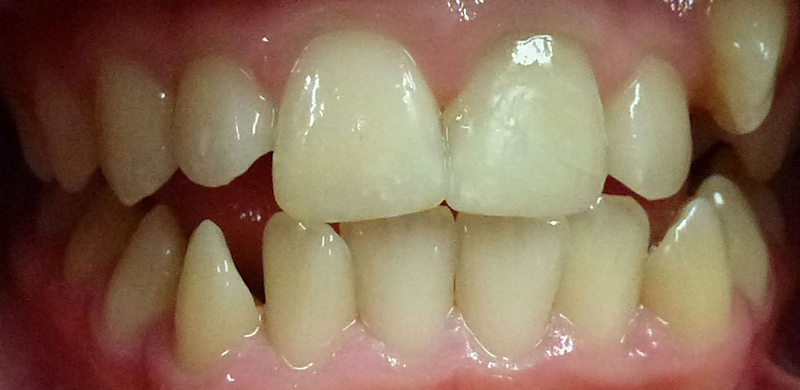 Teeth repaired using composite (white) filling material.
Teeth repaired using composite (white) filling material.
Before
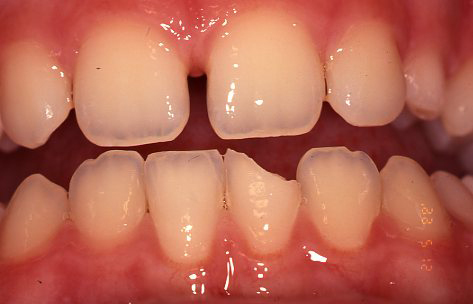 10 year old girl who was hit with a hurley broke lower front permanent tooth.
10 year old girl who was hit with a hurley broke lower front permanent tooth.
After
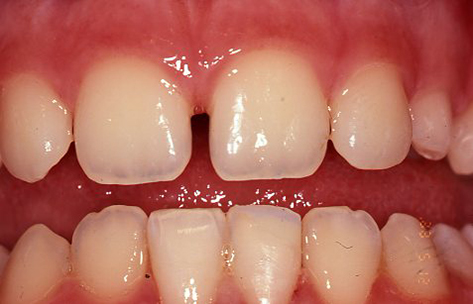 Tooth repaired using composite (white) filling material.
Tooth repaired using composite (white) filling material.
Before
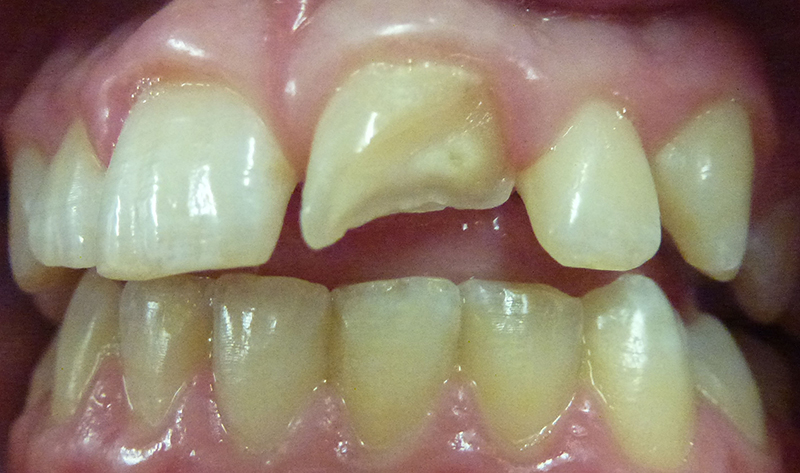 10 year old boy who fell while playing. Large fracture upper adult tooth (permanent central incisor).
10 year old boy who fell while playing. Large fracture upper adult tooth (permanent central incisor).
After
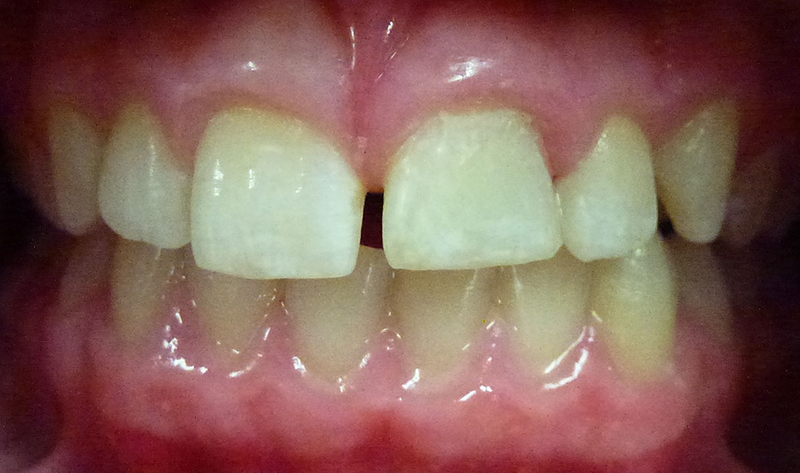 Tooth repaired using composite (white) filling material. This tooth subsequently required root canal treatment.
Tooth repaired using composite (white) filling material. This tooth subsequently required root canal treatment.
With extensive fractures of permanent teeth, there is a high risk of damage to the nerve!
Even after damaged teeth have been repaired, it is important that teeth are checked regularly by the Dentist.
In some cases there can be nerve / root damage, requiring further dental intervention.






