Galway Paediatric Dentist – Before & After Gallery
Oral Hygiene
Before
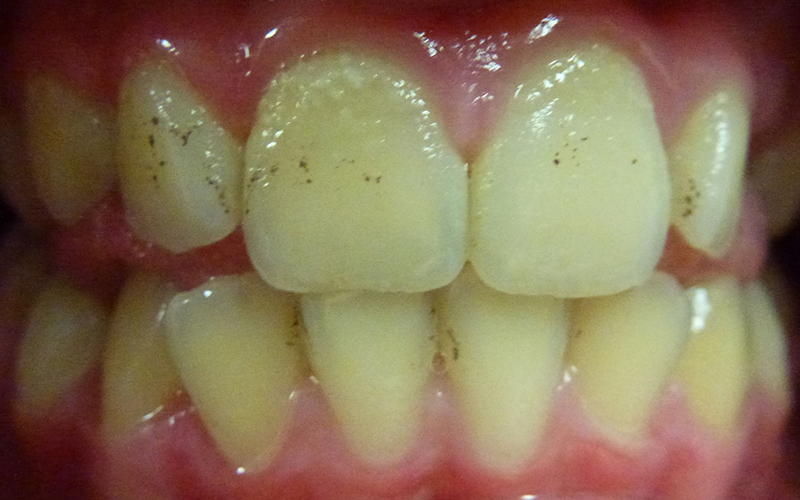 10 year old boy with plaque and staining on teeth (plaque is tooth coloured and can be difficult to see).
10 year old boy with plaque and staining on teeth (plaque is tooth coloured and can be difficult to see).
Disclosing Tablets
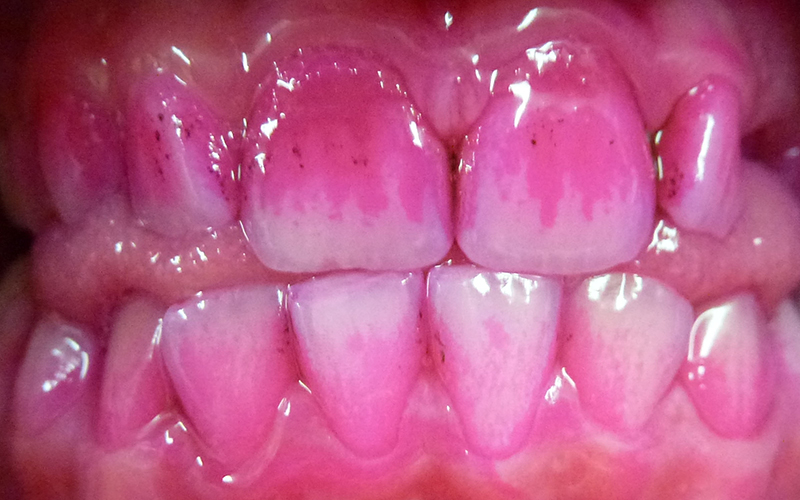 Disclosing tablets / solution shows the plaque missed at brushing.
Disclosing tablets / solution shows the plaque missed at brushing.
After
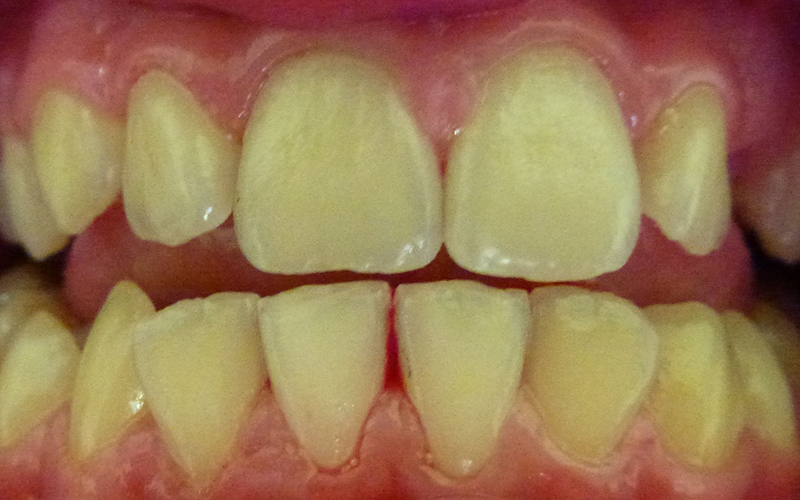 Plaque and stains removed by Dentist.
Plaque and stains removed by Dentist.
Before
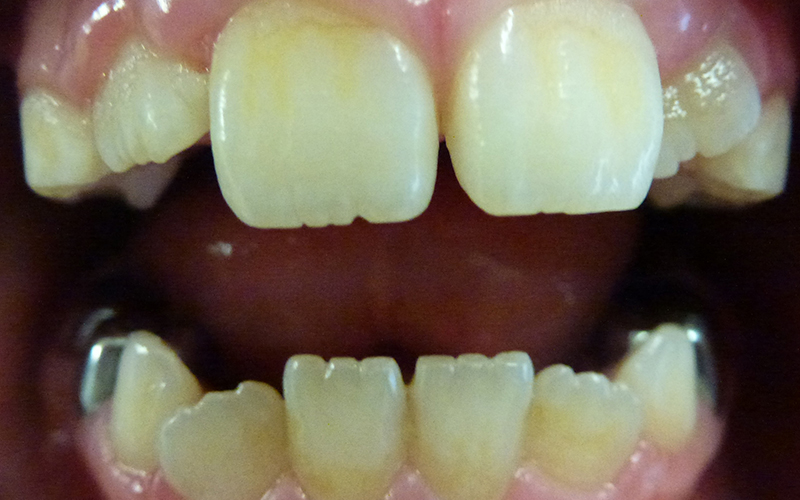 8 year old girl with yellow staining at gum lines.
8 year old girl with yellow staining at gum lines.
After
 Stains removed by Dentist.
Stains removed by Dentist.
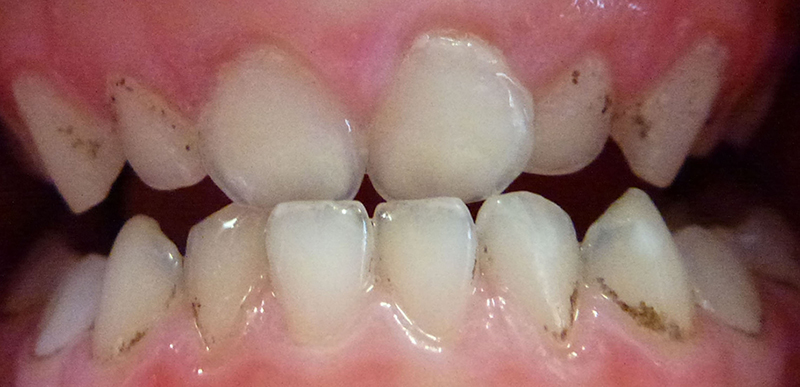
Before
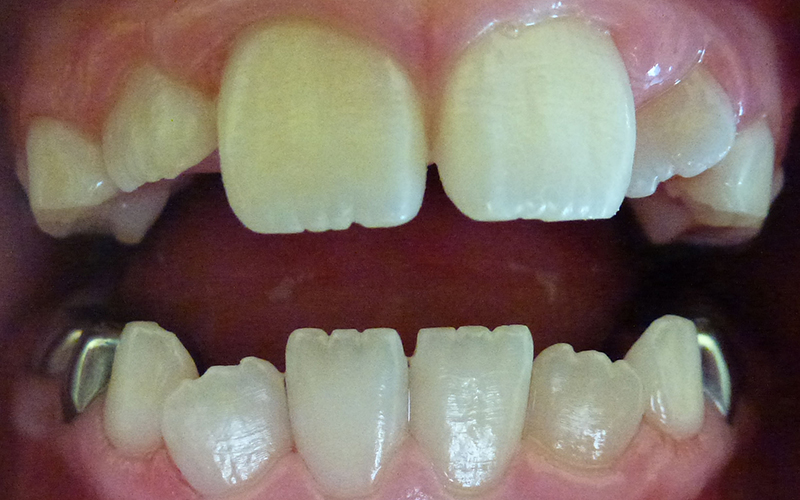
 12 year old girl with orthodontic appliances (braces). She thinks her teeth are clean but there is a lot of plaque present.
12 year old girl with orthodontic appliances (braces). She thinks her teeth are clean but there is a lot of plaque present.
Disclosing Tablets
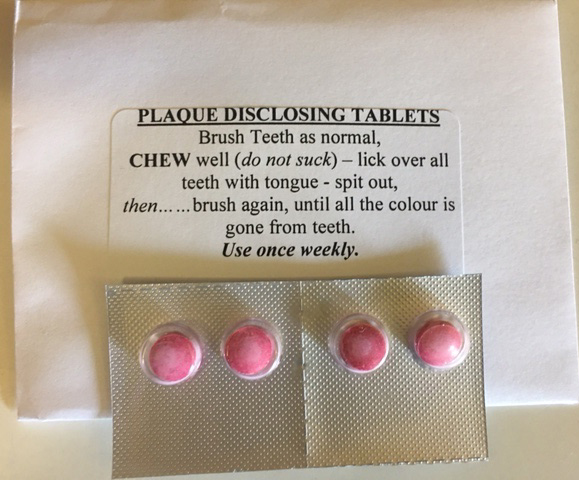 Disclosing tablets and directions for use.
Disclosing tablets and directions for use.
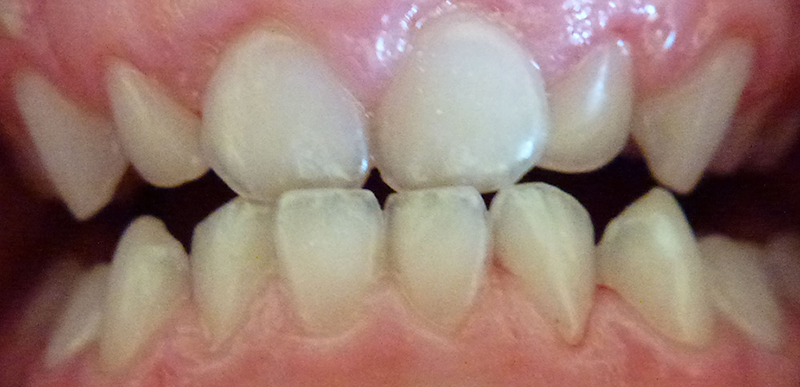
Disclosing Tablets Show Plaque
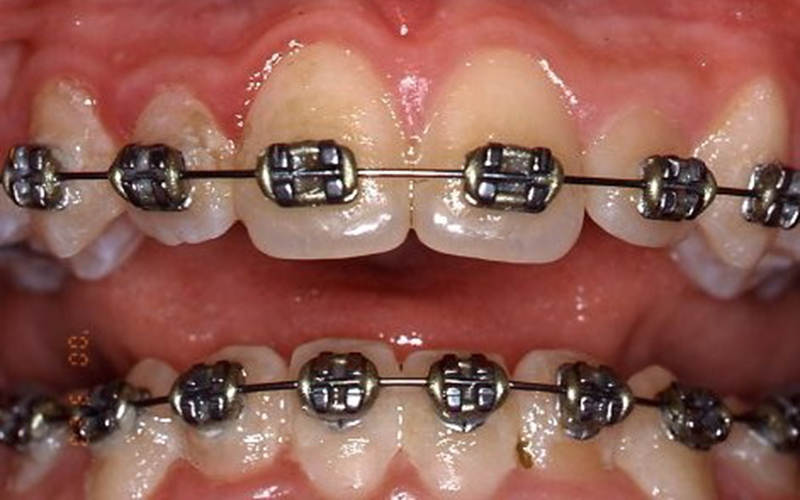
 Disclosing tablets / solution shows plaque very clearly. Easier for her to clean the teeth properly now.
Disclosing tablets / solution shows plaque very clearly. Easier for her to clean the teeth properly now.
Staining
Before
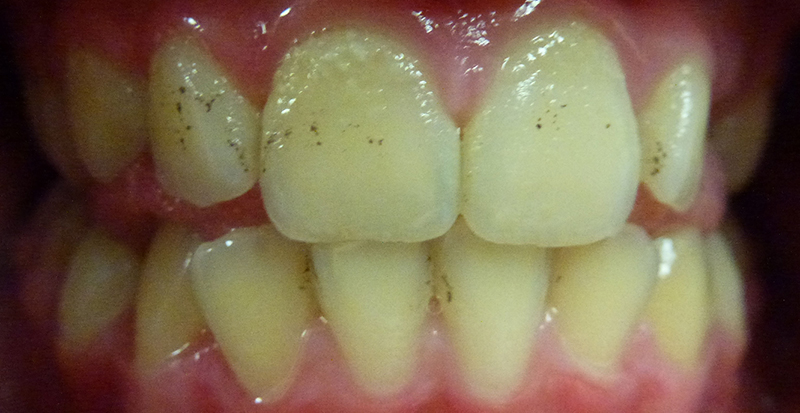 Child thought their teeth were clean, however, there is plaque build-up and staining especially on upper teeth.
Child thought their teeth were clean, however, there is plaque build-up and staining especially on upper teeth.
After
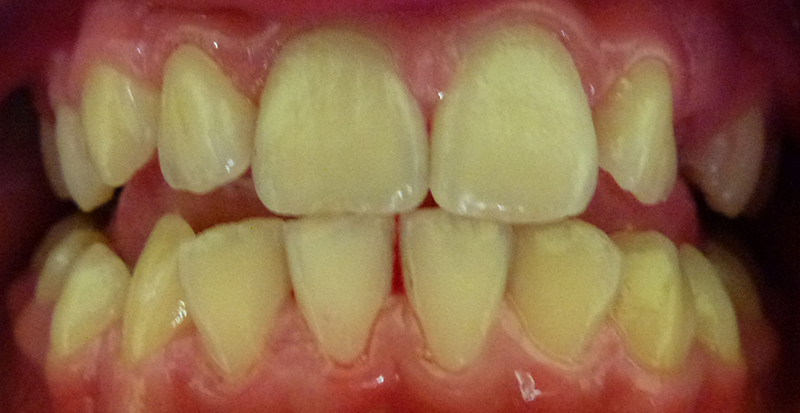 After cleaning by the Dentist.
After cleaning by the Dentist.
Before
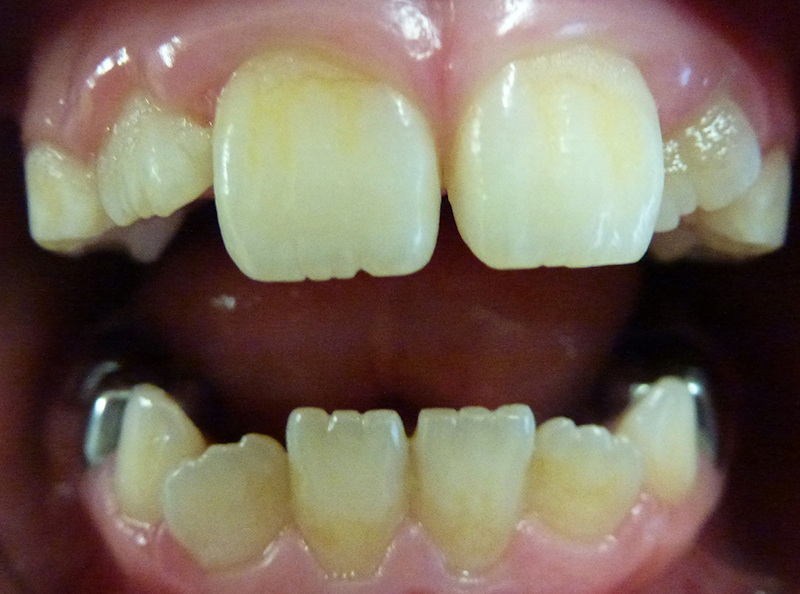 Children commonly miss brushing the gum line area. Build-up of plaque results in staining.
Children commonly miss brushing the gum line area. Build-up of plaque results in staining.
After
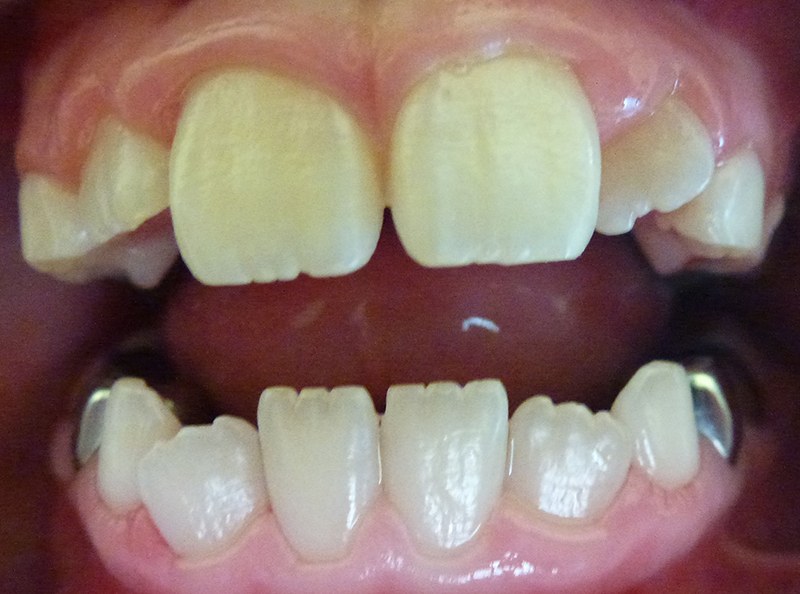 After cleaning by the Dentist.
After cleaning by the Dentist.
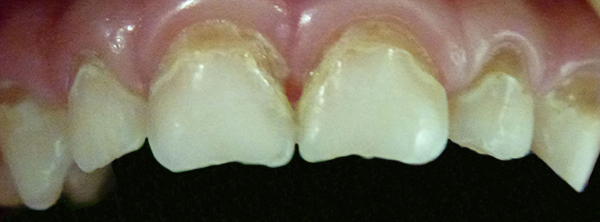
Before
 Chromogenic Staining – Some people have bacteria in their mouth that produce pigment, which stains teeth. This needs to be removed by a Dentist.
Chromogenic Staining – Some people have bacteria in their mouth that produce pigment, which stains teeth. This needs to be removed by a Dentist.
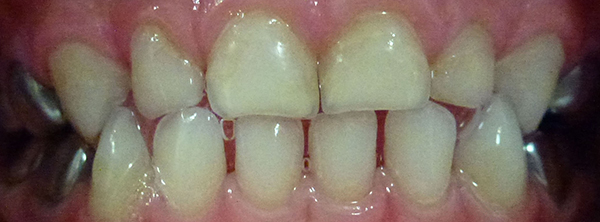
After
 After cleaning by the Dentist.
After cleaning by the Dentist.
Fissure Sealants
Before
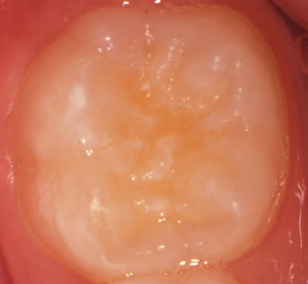
After
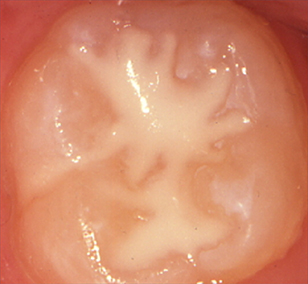
Fissure Sealing the deep pits and grooves on children’s molars, in particular 6 year molars (+ primary (baby) molars if required) greatly reduces the risk of tooth decay.
Fissure sealants are simple to apply and are cost effective.
Sealants need to be checked regularly by your dentist; usual preventive measures (cleaning, flossing, fluoride & low sugar diet etc.) are required to protect all other surfaces.
Early Childhood Caries (E.C.C.)
Progression of Untreated Dental Disease in Young Children
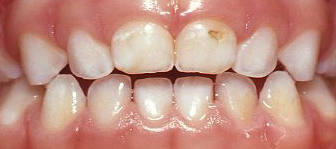 3 year old child who took a bottle of milk / formula / juice to bed at night. Tooth decay (cavities) visible on two top front teeth.
3 year old child who took a bottle of milk / formula / juice to bed at night. Tooth decay (cavities) visible on two top front teeth.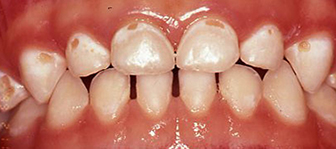 If child continues to take a bottle at night they will develop cavities on all top teeth and many other cavities on back teeth.
If child continues to take a bottle at night they will develop cavities on all top teeth and many other cavities on back teeth.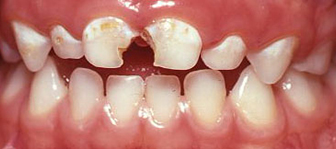 Left untreated, there is now further breakdown of teeth. Extensive dental treatment required.
Left untreated, there is now further breakdown of teeth. Extensive dental treatment required.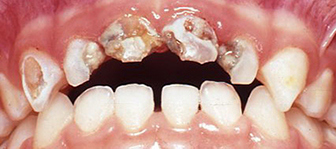 Bottle continued – 4 top teeth now need to be removed. Treatment also required on many other decayed back teeth. If not treated there is a high risk of abscess/pain/swelling and damage to the developing permanent teeth!
Bottle continued – 4 top teeth now need to be removed. Treatment also required on many other decayed back teeth. If not treated there is a high risk of abscess/pain/swelling and damage to the developing permanent teeth!Before
 5 year old child who was breast fed until 2 years – then took a bottle of milk to bed. This caused tooth decay on ALL of his 20 primary (baby) teeth.
5 year old child who was breast fed until 2 years – then took a bottle of milk to bed. This caused tooth decay on ALL of his 20 primary (baby) teeth.
After
 Teeth restored with white (composite) fillings and stainless steel crowns on his molars. (In conjunction with usual preventive and oral hygiene advice). He now has a healthy dentition and attends for regular dental check-ups.
Teeth restored with white (composite) fillings and stainless steel crowns on his molars. (In conjunction with usual preventive and oral hygiene advice). He now has a healthy dentition and attends for regular dental check-ups.
3 Year Old Twins
Decay in primary (baby) molars
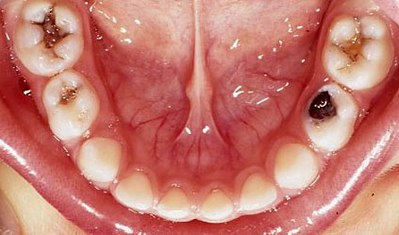 This child took a bottle of milk to bed – extensive tooth decay on all molars…
This child took a bottle of milk to bed – extensive tooth decay on all molars…
Healthy primary (baby) molars
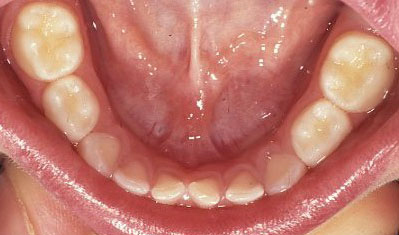 …Her twin only took plain water to bed and all teeth are healthy
…Her twin only took plain water to bed and all teeth are healthy
Silver Diamine Fluoride
BEFORE application of SDF
 Back baby (primary) molars with tooth decay
Back baby (primary) molars with tooth decay
– BEFORE application of SDF
AFTER application of SDF
 Back baby (primary) molars with tooth decay
Back baby (primary) molars with tooth decay
– AFTER application of SDF
BEFORE application of SDF
 Front (primary) teeth with tooth decay
Front (primary) teeth with tooth decay
– BEFORE application of SDF
AFTER application of SDF
 Front (primary) teeth with tooth decay
Front (primary) teeth with tooth decay
– AFTER application of SDF
Tooth decay is an infectious bacterial disease!
Use of bottles with milk, juice or formula and prolonged breast feeding are the main causes of decay in baby teeth.
If your child takes a bottle to bed – the ONLY safe drink is PLAIN WATER
White Fillings
Before
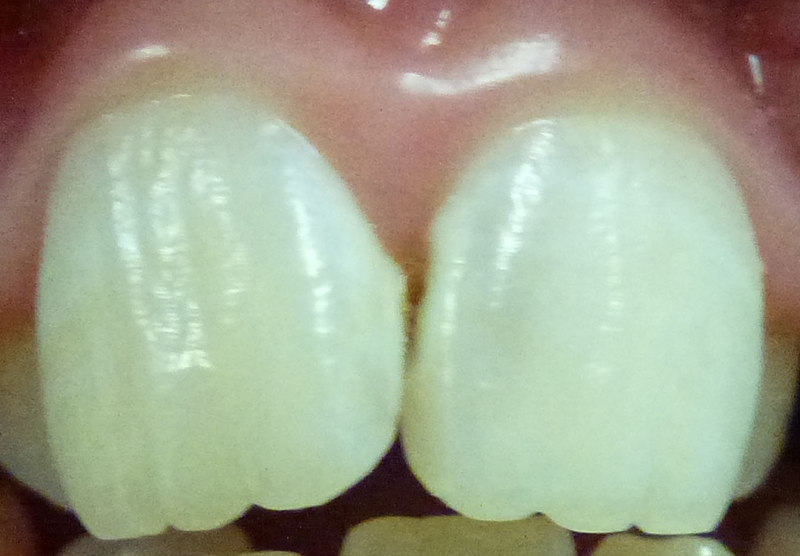 11 year old girl with decay between front teeth. Very high sugar intake combined with previous poor oral hygiene.
11 year old girl with decay between front teeth. Very high sugar intake combined with previous poor oral hygiene.
During Treatment
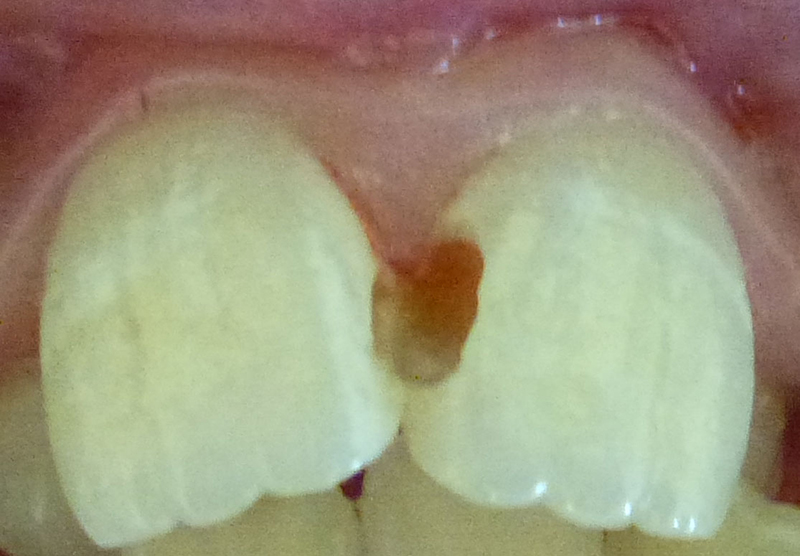 One cavity is much larger than it initially appeared.
One cavity is much larger than it initially appeared.
After
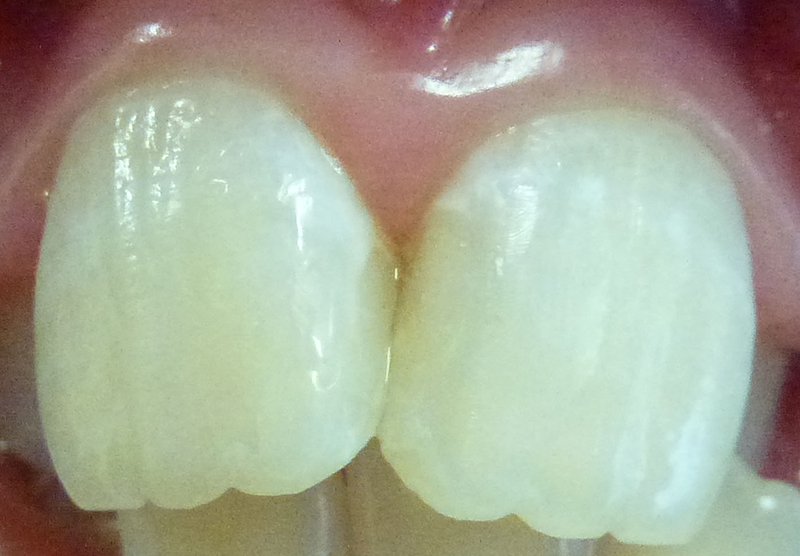 Teeth after composite (white) fillings.
Teeth after composite (white) fillings.
Neither child nor parents knew there were cavities here! It is important to have regular dental check-ups.
Before
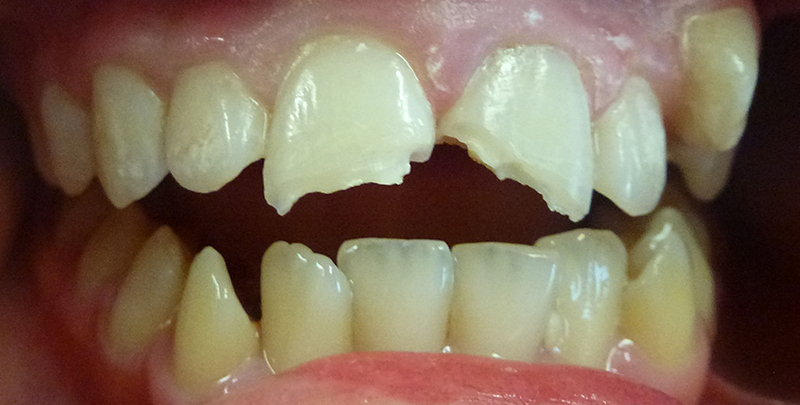 Young boy who fractured 2 upper permanent (adult) front teeth.
Young boy who fractured 2 upper permanent (adult) front teeth.
After
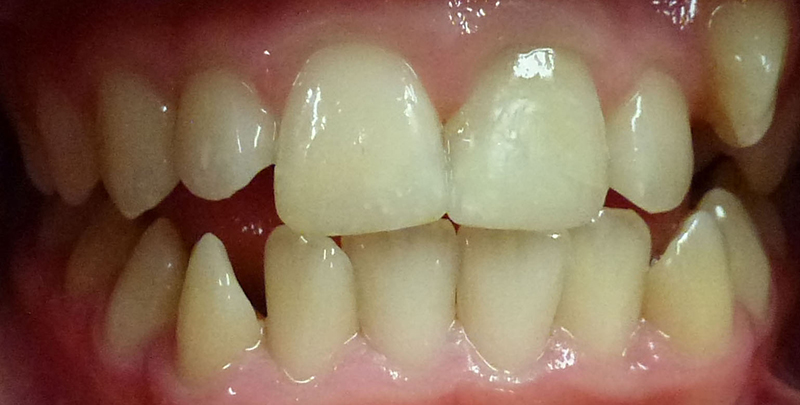 Teeth restored with composite (white) fillings.
Teeth restored with composite (white) fillings.
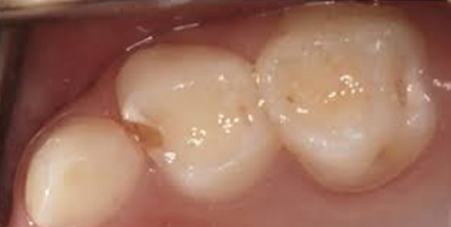
Before
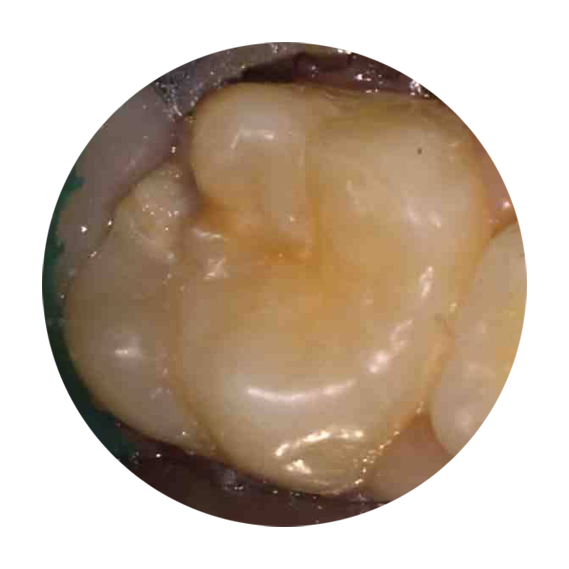 Tooth decay in 6 year molar (permanent tooth). Parent & child unaware of any decay.
Tooth decay in 6 year molar (permanent tooth). Parent & child unaware of any decay.
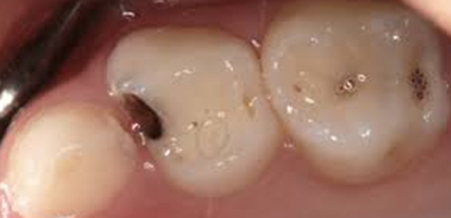
Tooth Decay Removed
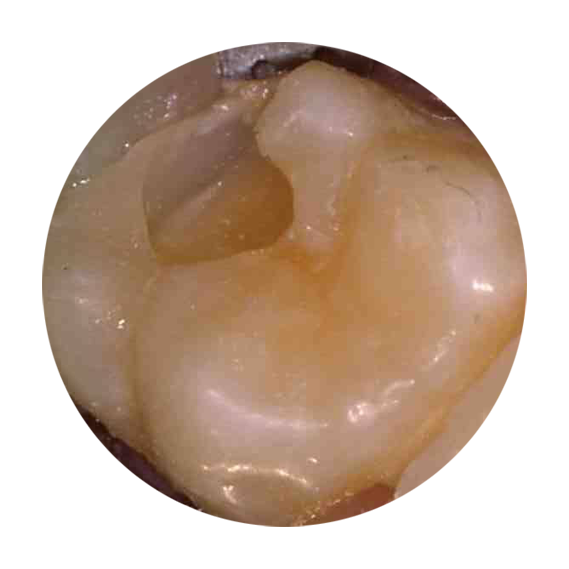 Once tooth decay was removed, the cavity was much larger than it initally appeared.
Once tooth decay was removed, the cavity was much larger than it initally appeared.
After
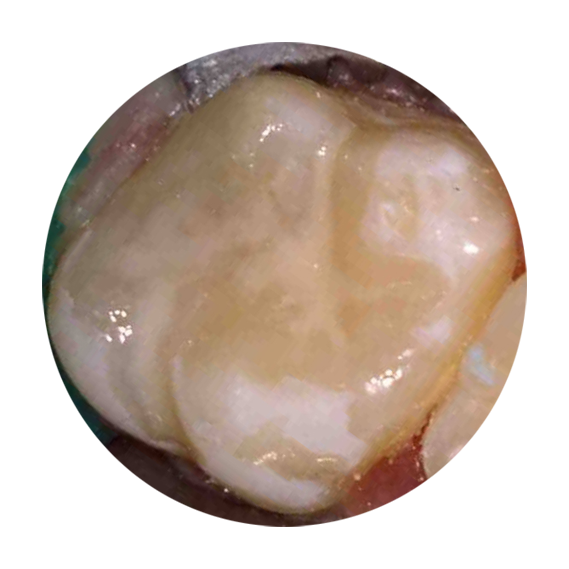 Cavity restored with Composite (white). Filling and all pits and grooves fissure sealed.
Cavity restored with Composite (white). Filling and all pits and grooves fissure sealed.
Our material of choice is Composite (white filling)
Trauma to Primary (Baby) Teeth
TRAUMA = Dental trauma is common in children.
It is important that oral / dental injuries are checked by the Dentist as soon as possible.
Before
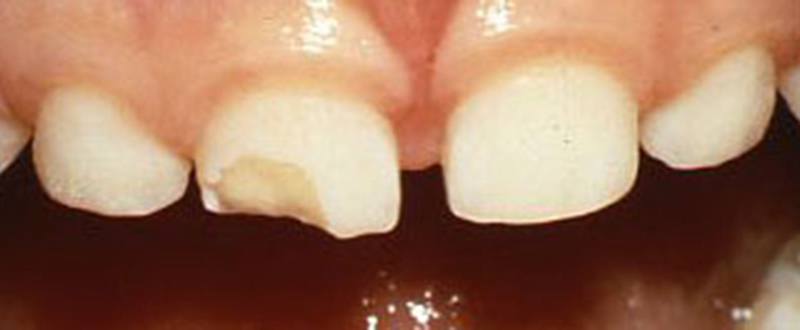 3 year old girl who fell and broke her upper primary (baby) tooth.
3 year old girl who fell and broke her upper primary (baby) tooth.
After
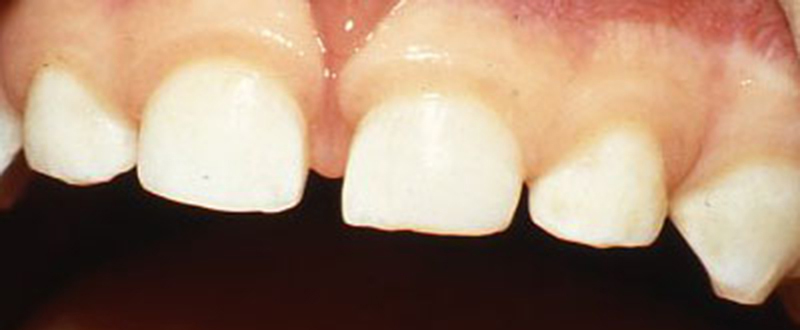 Repaired with composite (white) filling material.
Repaired with composite (white) filling material.
Trauma To Baby Teeth
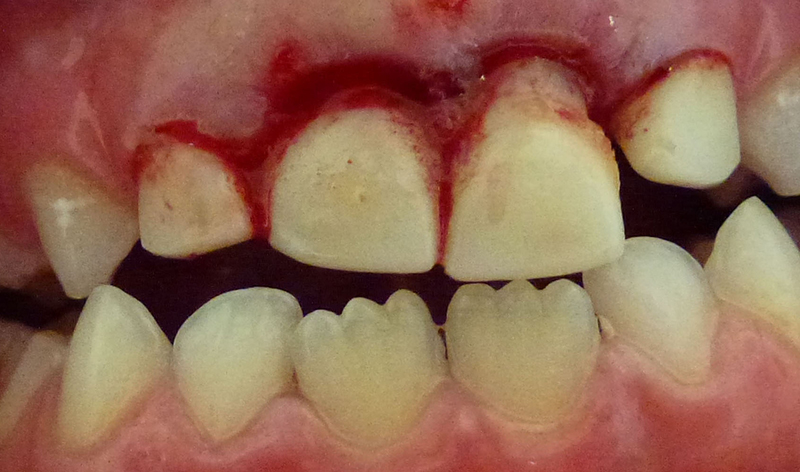 6 year old boy who fell off his bike and bumped his two front primary (baby) teeth.
6 year old boy who fell off his bike and bumped his two front primary (baby) teeth.
Permanent Teeth Erupting
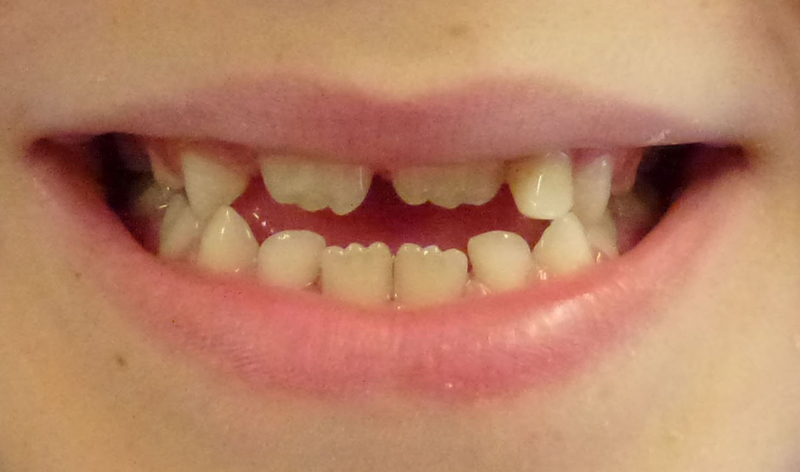 3 months later, all recovered and permanent (adult) teeth have erupted into correct position.
3 months later, all recovered and permanent (adult) teeth have erupted into correct position.
Defects on Permanent (Adult) Teeth
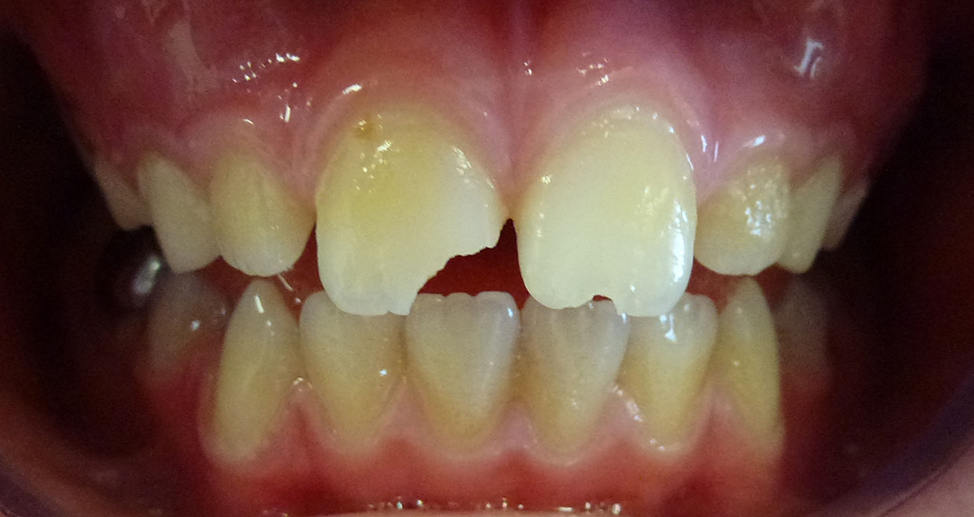
 The original trauma to his primary (baby) teeth had damaged his permanent (adult) front teeth.
The original trauma to his primary (baby) teeth had damaged his permanent (adult) front teeth.
Repaired Defects
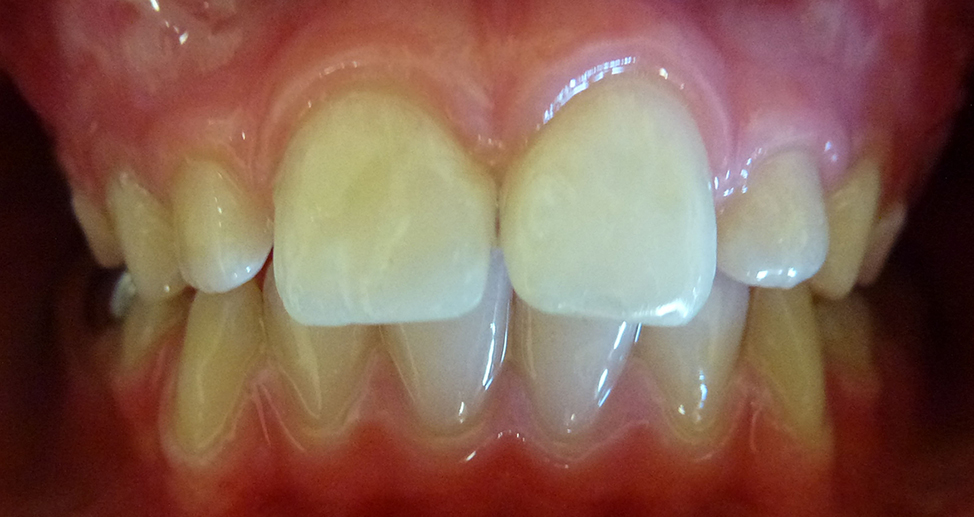
 This was easily repaired with composite (white) filling material.
This was easily repaired with composite (white) filling material.
Damage to the edges of permanent (adult) front teeth in a young child, caused by injury to their primary (baby) teeth at a very young age (approx. 1-2 years). It is important that a Dentist checks your child if they injure their teeth / mouth.
Trauma to Permanent Teeth
Before
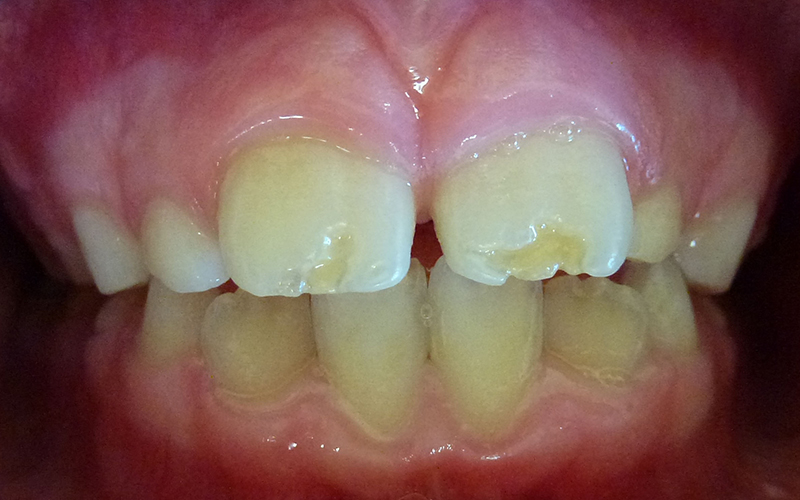
 8 year old girl, who fell playing on concrete, fractured 2 upper permanent (adult) teeth, one tooth fractured more extensively than the other.
8 year old girl, who fell playing on concrete, fractured 2 upper permanent (adult) teeth, one tooth fractured more extensively than the other.
After
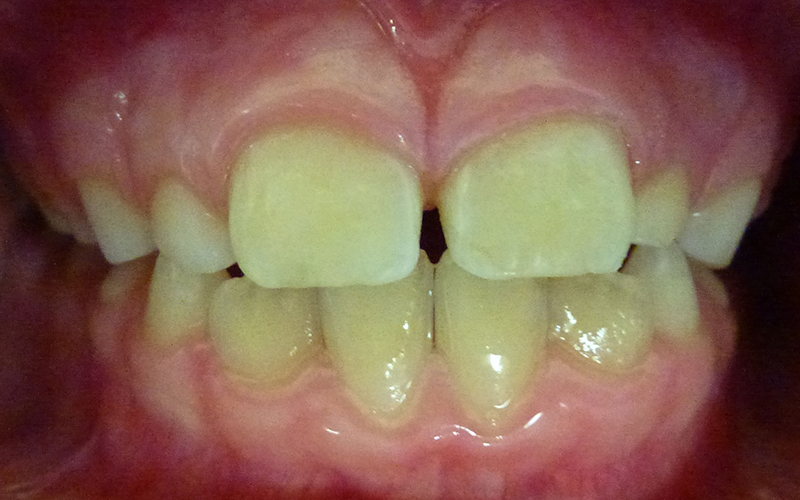
 Both teeth repaired using composite (white) filling material.
Both teeth repaired using composite (white) filling material.
Before
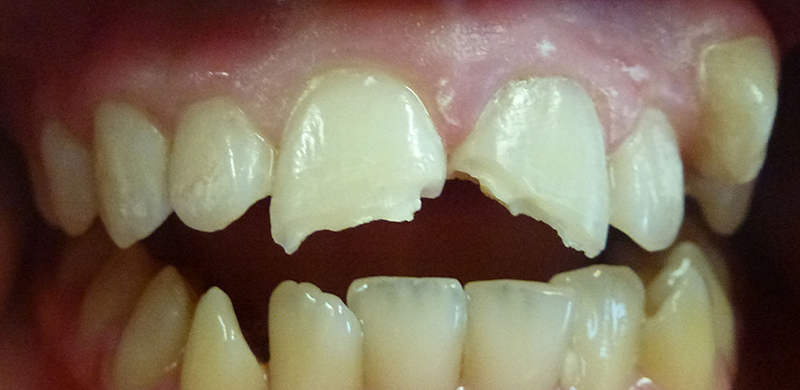 13 year old boy who fell playing sport, broke 2 upper permanent (adult) teeth.
13 year old boy who fell playing sport, broke 2 upper permanent (adult) teeth.
After
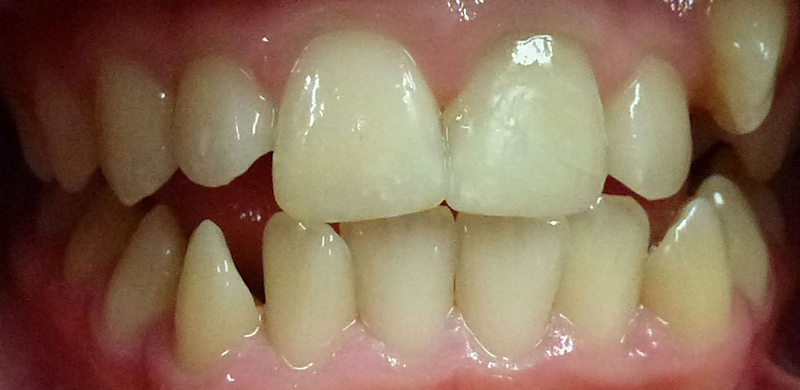 Teeth repaired using composite (white) filling material.
Teeth repaired using composite (white) filling material.
Before
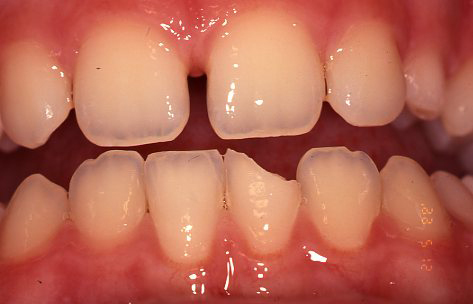 10 year old girl who was hit with a hurley broke lower front permanent tooth.
10 year old girl who was hit with a hurley broke lower front permanent tooth.
After
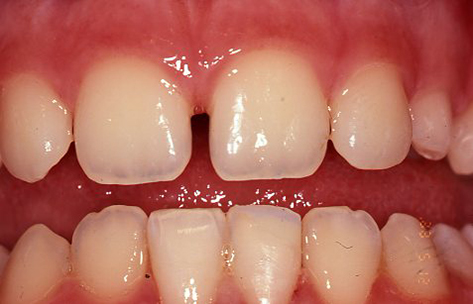 Tooth repaired using composite (white) filling material.
Tooth repaired using composite (white) filling material.
Before
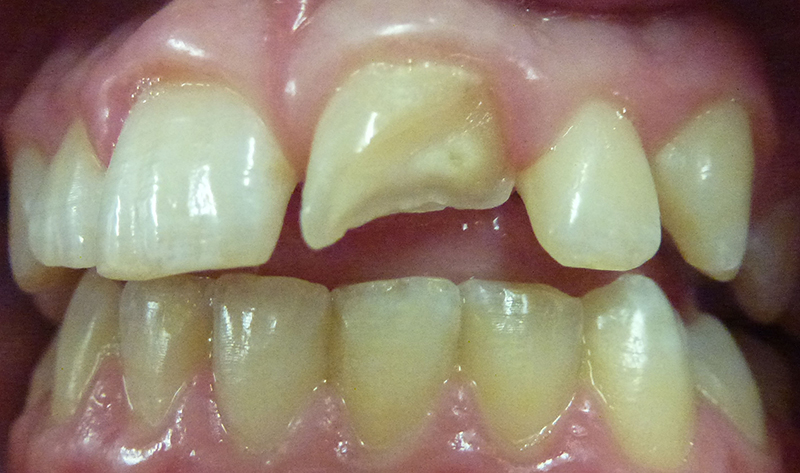 10 year old boy who fell while playing. Large fracture upper adult tooth (permanent central incisor).
10 year old boy who fell while playing. Large fracture upper adult tooth (permanent central incisor).
After
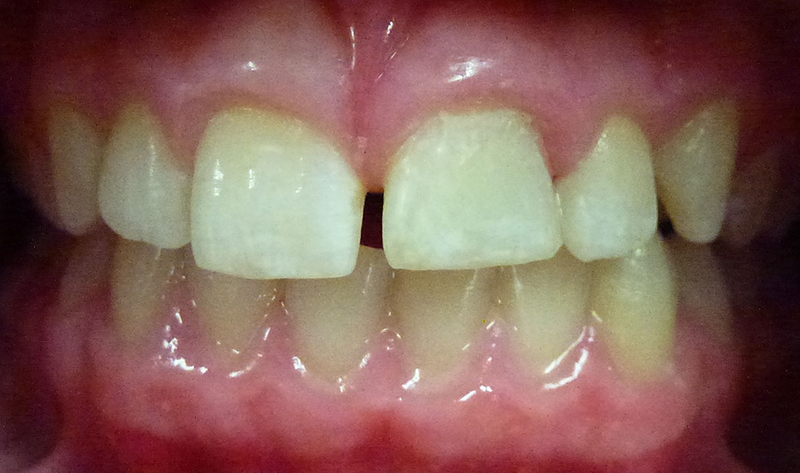 Tooth repaired using composite (white) filling material. This tooth subsequently required root canal treatment.
Tooth repaired using composite (white) filling material. This tooth subsequently required root canal treatment.
With extensive fractures of permanent teeth, there is a high risk of damage to the nerve!
Even after damaged teeth have been repaired, it is important that teeth are checked regularly by the Dentist.
In some cases there can be nerve / root damage, requiring further dental intervention.
Abscess
Abscess on the upper gum
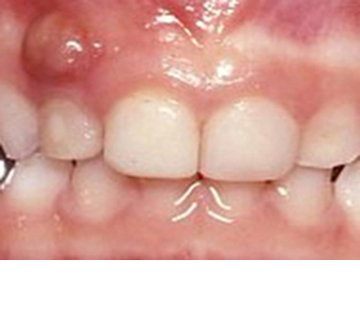
An abscess is an infection which indicates the nerve of the tooth is dead. This can present as a “gumboil” or swelling on the gum. It is most commonly caused by severe tooth decay which has progressed close to or into the nerve.
Model of developing teeth in a 3 year old child
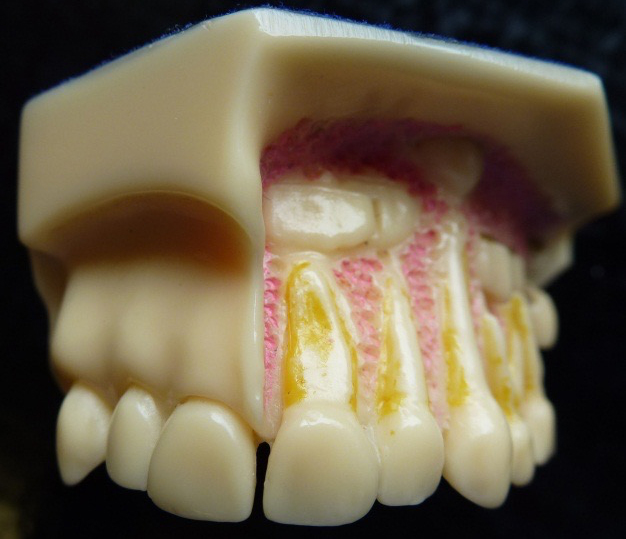
The permanent incisor develops very close to the root of the primary incisor so an abscess on a baby tooth can damage the developing permanent tooth.
Another cause of an abscess is where there has been injury to the nerve as a result of a bump or fracture of the tooth. An abscess does not necessarily cause pain.
Abscesses on baby teeth need to be treated
Mamelons
Upper permanent central (adult) incisor
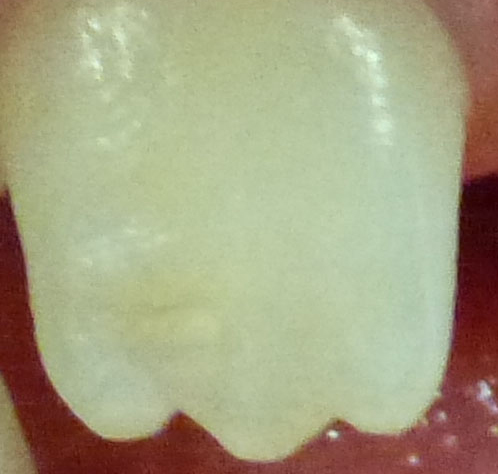 Mamelons are rounded protuberances on the cutting edge of new permanent incisor teeth.
Mamelons are rounded protuberances on the cutting edge of new permanent incisor teeth.
Lower permanent (adult) central incisors
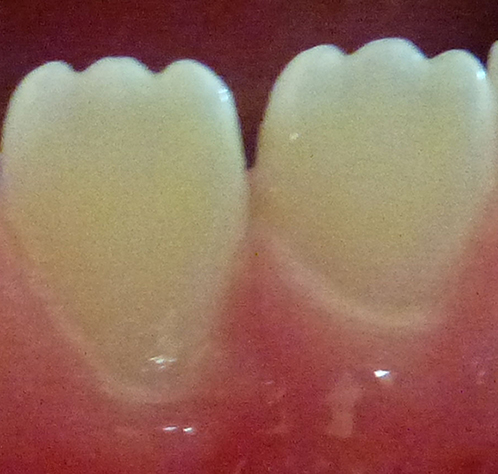 These are a normal anatomical feature of young teeth and wear away with use. (Adults no longer have mamelons). Mamelons can vary considerably in size but even when pronounced are usually of no clinical significance.
These are a normal anatomical feature of young teeth and wear away with use. (Adults no longer have mamelons). Mamelons can vary considerably in size but even when pronounced are usually of no clinical significance.
Habits
Correct Position of Baby Teeth
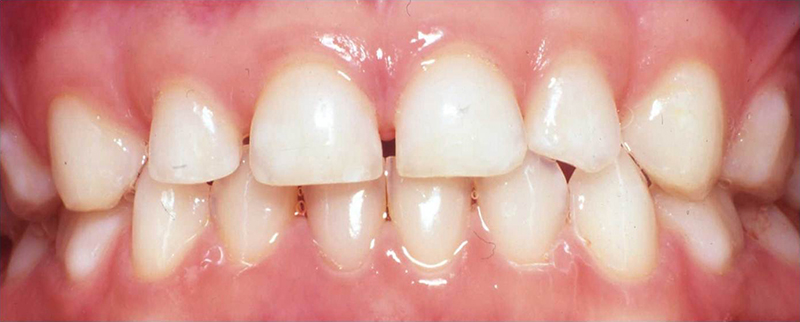 All teeth touching evenly.
All teeth touching evenly.
Incorrect Position of Teeth
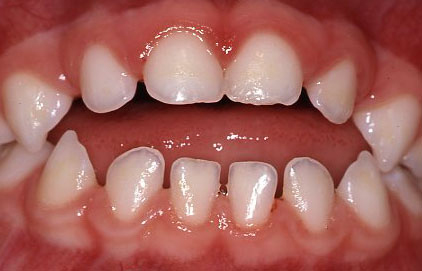 This child used a soother. Back teeth are closed but unable to close front teeth. This affects speech (e.g. lisping) and ability to bite with their front teeth.
This child used a soother. Back teeth are closed but unable to close front teeth. This affects speech (e.g. lisping) and ability to bite with their front teeth.
Incorrect Position of Teeth
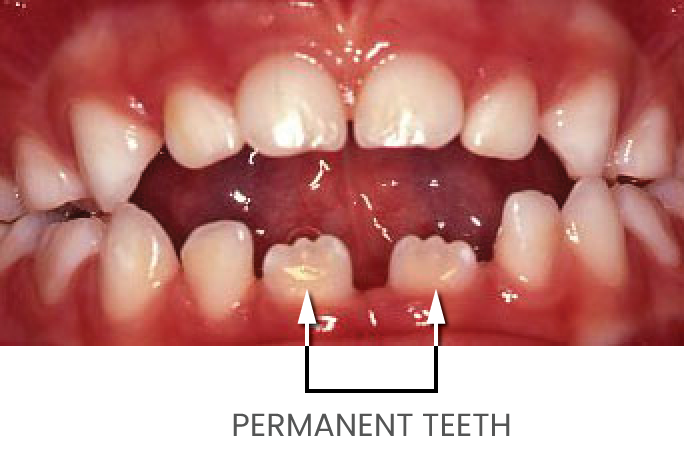 6 year old child – still sucking their thumb. Because of this the permanent (adult) teeth are unable to grow into their correct position.
6 year old child – still sucking their thumb. Because of this the permanent (adult) teeth are unable to grow into their correct position.
Child Sucking Thumb
 Child sucking their thumb, resulting in incorrect positioning of teeth.
Child sucking their thumb, resulting in incorrect positioning of teeth.
Incorrect Position of Teeth
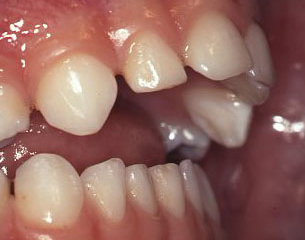 Side view of young child with teeth projected forward – “buck teeth”. Unsightly appearance and higher risk of trauma.
Side view of young child with teeth projected forward – “buck teeth”. Unsightly appearance and higher risk of trauma.
Children are actively growing so if habits persist they can rapidly damage the position of the teeth, alter the shape of the dental arches and can also affect their speech. We would recommend all habits are discouraged by 1 – 2 years of age.
Treatment can be costly to correct at a later stage.
Molar Incisor Hypomineralisation (M.I.H)
See article linked for further information (IDA)
This is the name given to a dental condition where the enamel on children’s first permanent molars (i.e. 6 year molars) and permanent incisors (front teeth) does not form correctly.
“Hypomineralisation” means under-mineralised.
The teeth can look discoloured (e.g. cream/brown marks) and if severe the molars can break down and become quite sensitive. Children may complain of sensitivity when consuming cold foods/drinks or when brushing their teeth. In many cases parents may be the first to notice a “discolouration” of tooth/teeth.
Note: There are a number of other reasons for discolouration or sensitivity of teeth eg. Tooth decay, fracture etc.
It is very important that all tooth discolouration is checked!
1st Permanent Molar (6 year molar)
• Mild M.I.H.
Note: this tooth has been fissure sealed.

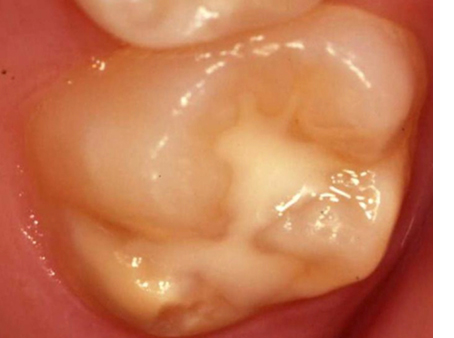
1st Permanent Molar (6 year molar)
• Mild M.I.H.
Note: this tooth has been fissure sealed.
1st Permanent Molar (6 year molar)
• Moderate M.I.H.
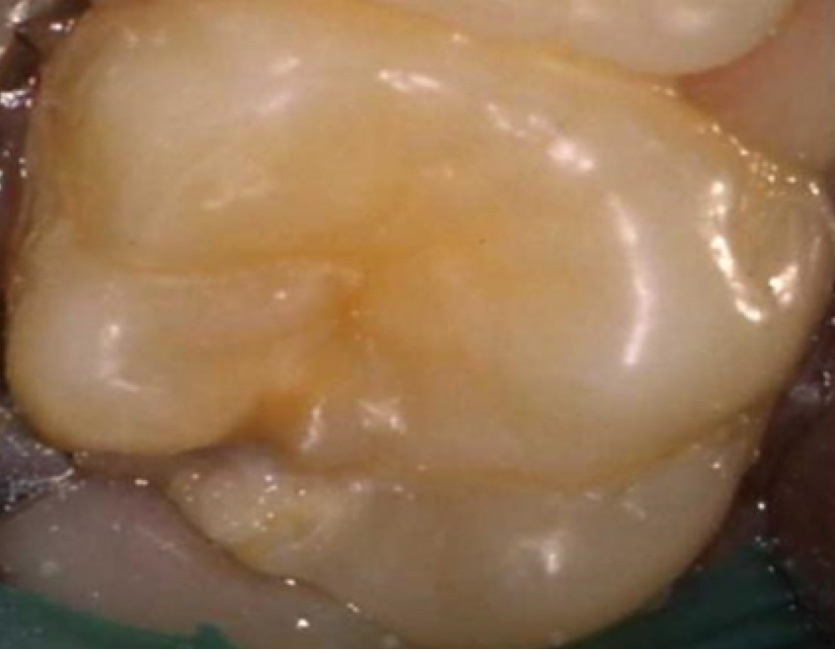 Defective area of enamel.
Defective area of enamel.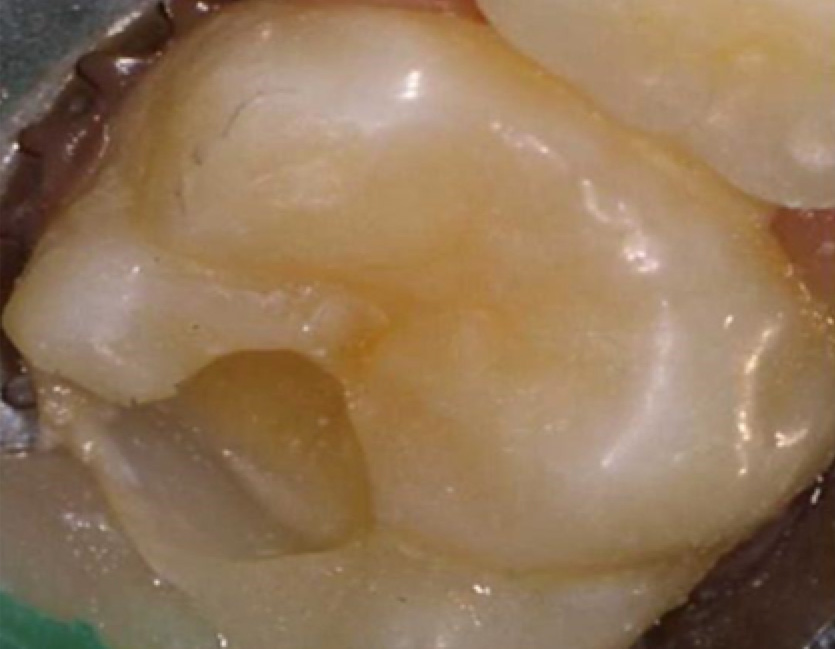 When defect / tooth decay removed,
When defect / tooth decay removed,the cavity is much larger.
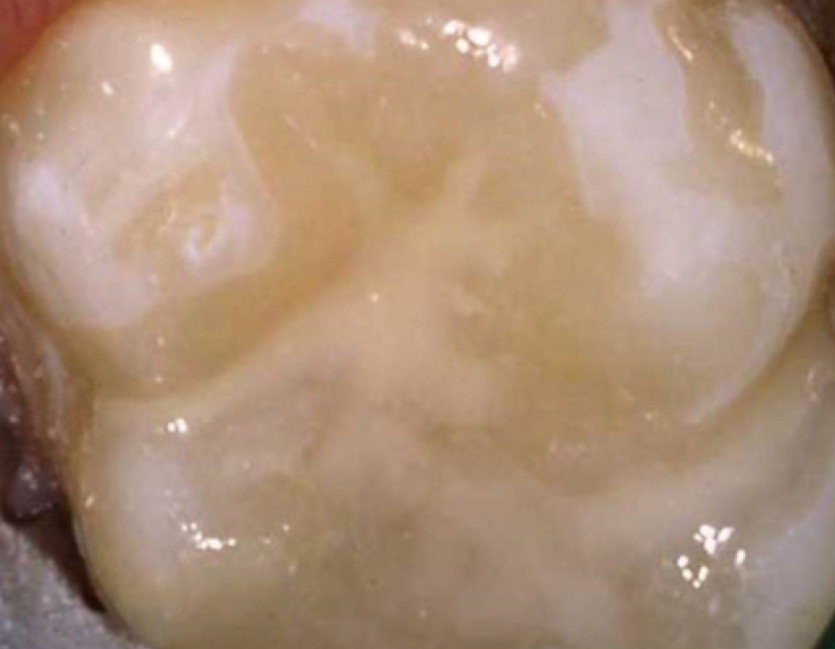 Cavity successfully repaired with a permanent
Cavity successfully repaired with a permanentwhite filling (composite).
Note: these teeth must be checked regularly
by a dentist.
1st Permanent Molar (6 year molar)
• Moderate – Severe M.I.H.
These teeth are too damaged to be successfully restored (long-term) with white fillings. The options for these teeth are restoration with a crown or extraction.
1. Restoration with a stainless steel crown (SSC)
Severe – Before Treatment
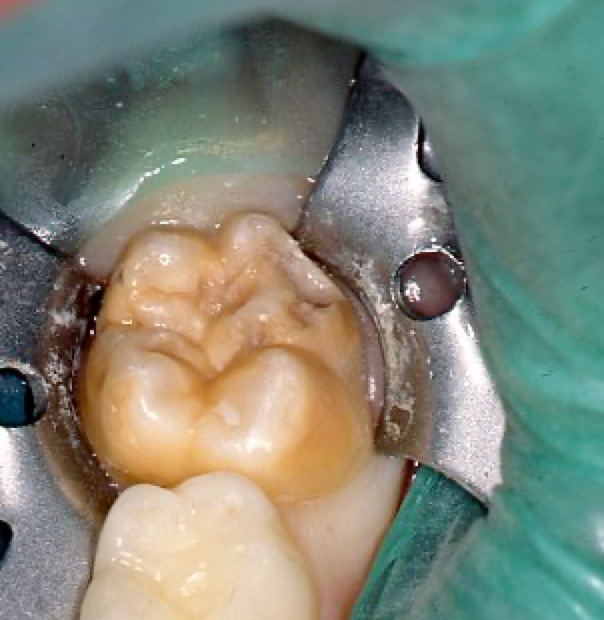 Defective permanent tooth.
Defective permanent tooth.
Healthy primary (baby) tooth.
After Treatment – Stainless Steel Crown
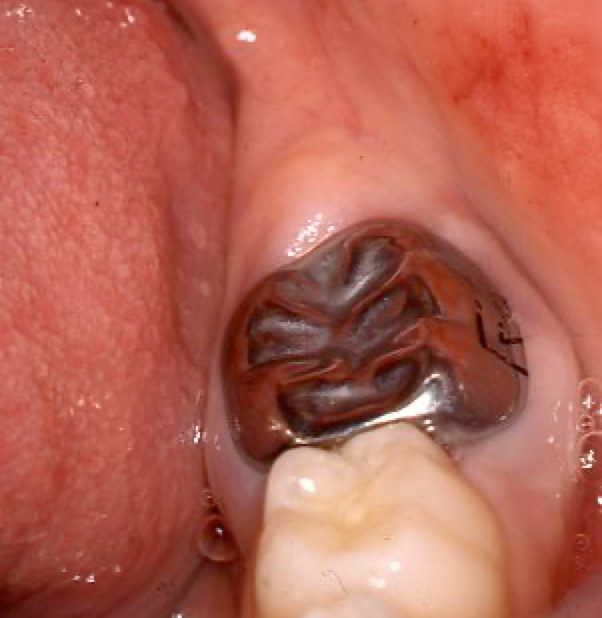
Full coverage of tooth with a metal crown protects it for many years.
(These crowns do need to be replaced when patient is in their early twenties).
2. Extraction of some or all four severely hypomineralised first permanent molars (6 year molars)
We find it very helpful to get the opinion of an orthodontist (specialist in braces) before proceeding with extraction of permanent molars.
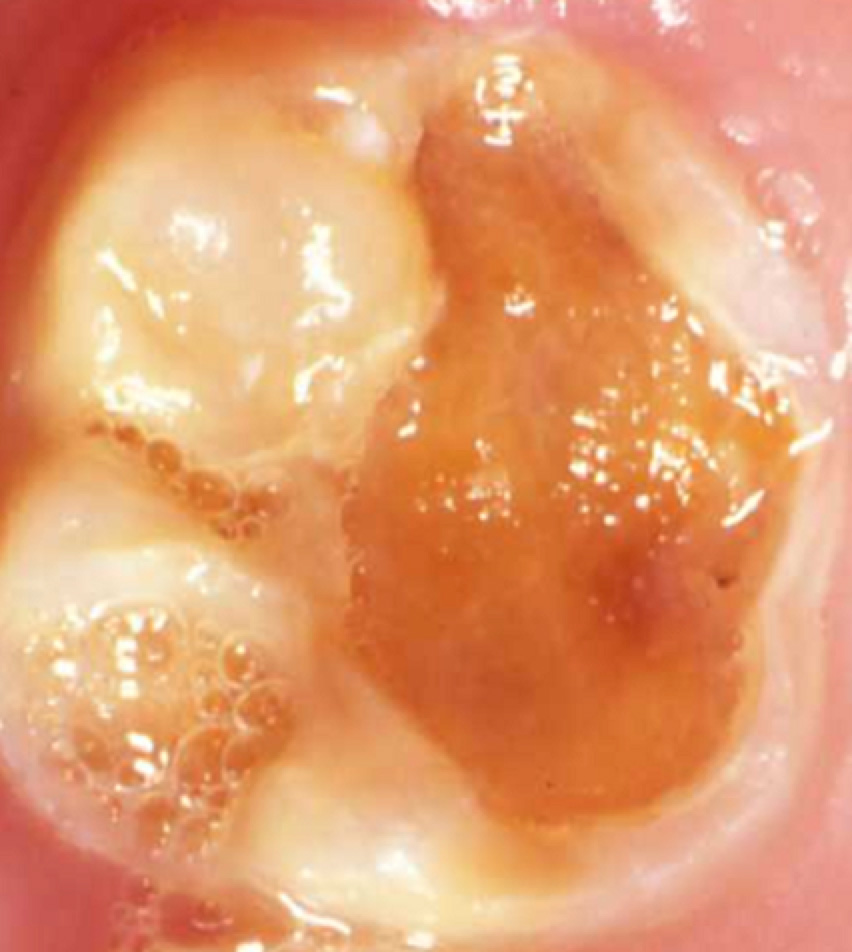
If teeth are very damaged / or affecting the nerve – their long term prognosis is poor – so can be best to extract them.
If done at the correct time, the next molar (12 year molar) will move nicely into the extraction space.
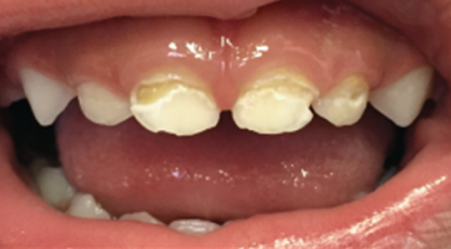
Permanent Incisor – 8 year old child
• Mild discolouration of permanent front tooth.
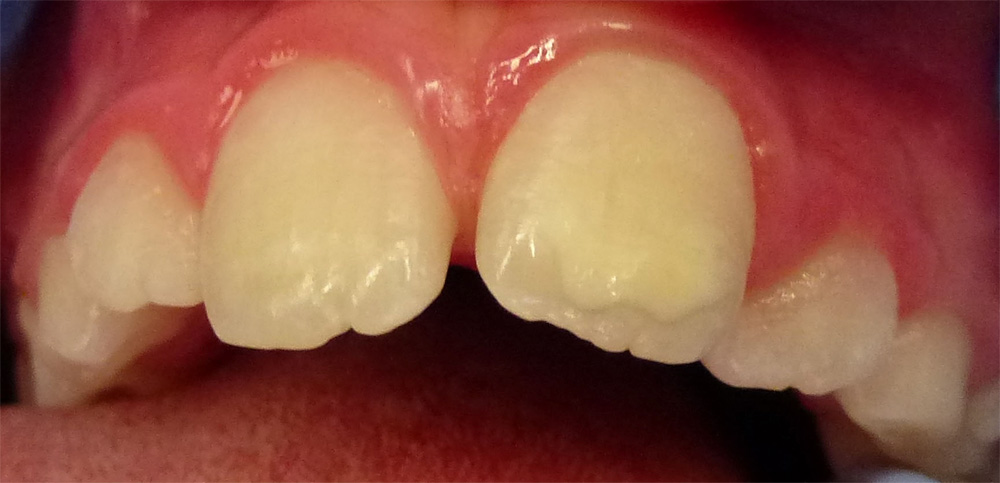
No Treatment Required
Permanent Incisor – 8 year old child
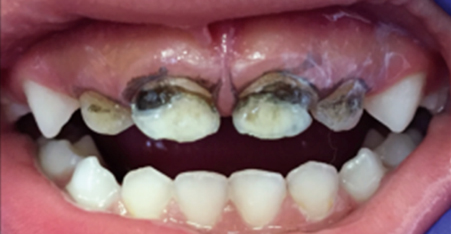
• Moderate discolouration of permanent front tooth in a child with M.I.H.
Appearance can be improved with composite (white filling material); little / no tooth structure is removed.
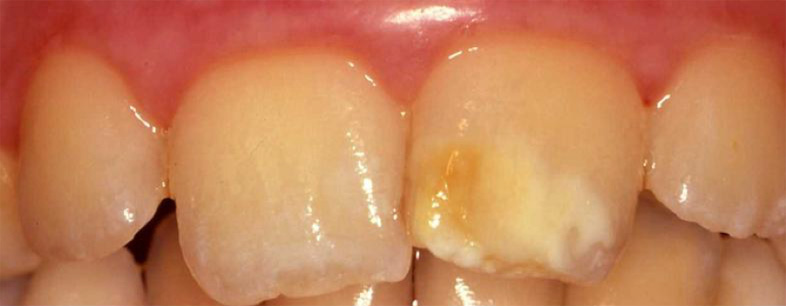
Before Treatment
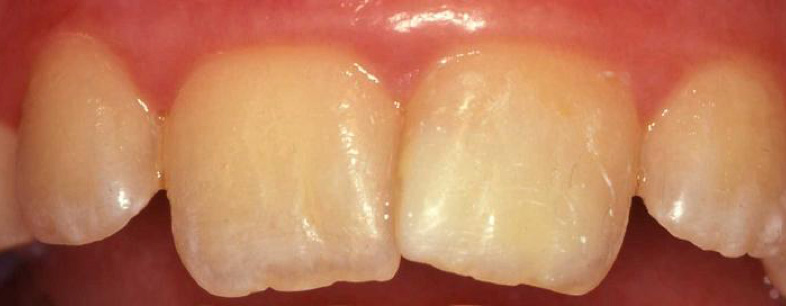
After Treatment
“Masking” with white filling material (composite)
In later years, patient may choose another treatment, e.g. composite / porcelain veneer.






